Athlete's foot is one of the most common infections. The fungus on the legs is distinguished by its vitality and ease of development. If you rely on statistics, then 20% of the world's population suffers from the fungus.
What is a skin fungus?
Fungal diseases are infectious diseases that affect the skin. The most common type of fungus is mycosis. In medicine, this skin disease is divided into several types.
The fungus can adapt to almost any habitat. Fungal spores can survive for a long time in ordinary clothing or shoes. In most cases, fungal infections are exposed to the feet and nail plates on a person's legs.
How does a mycosis progress?
The causative agent of foot mycosis is the fungus Trichophyton rubrum, T. Mentagrophytes and Epidermophyton floccosum. Mycosis can be transmitted through contact with infected skin or after using personal hygiene items.
Mycosis is characterized by the destruction of the skin in the form of peeling. This is because the fungus penetrates deep under the skin, causing damage to the epidermis.
Yellow or white spots may appear on the nails. When the fungus affects the toes, small blisters with liquid form between them, which burst, healing is painful. Athlete's foot is also accompanied by an unpleasant smell. Symptoms of mycosis can vary depending on the species. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with each of them in more detail.
The main forms of mycosis:
- interdigital mycosis.
- Squamous hyperkeratotic form.
- vesicular shape.
- Deleted form.
- nail fungus.
interdigital mycosis
The most common localization of the interdigital fungus is the intervals between 3, 4 and 5 toes.
The main symptoms of interdigital mycosis:
- The formation of a crack covered with a white flaky thick film.
- A small amount of liquid may be released from the crack.
- The appearance of diaper rash between the toes.
- Slight itching between fingers.
Initially, the fungus may be dormant between the toes without any symptoms. But gradually changes are observed - the skin becomes dry and rough, acquires a gray tint, cracks appear in coarsened areas.
In addition, there is a so-called "wet" fungus between the fingers. This form is characterized by the formation of fluid-filled blisters. These blisters burst, thereby creating the effect of a "wet" fungus. Such a fungus is most commonly formed after wearingtight, non-ventilated shoes, as well as in periods of heavy loads.
Squamous hyperkeratotic form
The squamous-hyperkeratotic form of mycosis is characterized by severe detachment and keratinization of the skin. This form of mycosis is very common, but it most often affects people with atopic dermatitis.
The main symptoms of the squamous-hyperkeratotic form of mycosis:
- Weak itching.
- The formation of cracks in the skin of the feet.
- Pains.
- dryness of the skin.
- exfoliation of the skin.
- Erythema with clear borders.
- Yellow scales.
- Onychomycosis - damage to the nail plates.
vesicular shape
The vesicular form of the fungus is the rarest of all. Only 8% of all patients with mycosis are exposed to this type of disease. The vesicular form is characterized by the formation of rashes with liquid contents inside. When these vesicles rupture, erosion occurs, which can become infected.
The main symptoms of bladder fungus:
- Formation of blisters of red or pink color.
- In the formations there is a liquid of transparent color.
- The size of the bubbles can reach a maximum of 1 cm in diameter.
- The rash may be accompanied by mild itching.
- Wet Bubbles.
This form of mycosis is dangerous because there is a high probability of getting under the skin harmful bacteria and infections. To determine the vesicular form of mycosis, it is necessary to conduct special examinations and conduct a skin scraping for analysis, since external symptoms can easily confuse this disease with eczema or pustular psoriasis.
Deleted form
The erased form of the fungus is almost always the beginning of the development of foot diseases - mycoses.
With the erased form of the fungus there are practically no visible symptoms, but some of them can still be distinguished:
- The skin between the toes peels off easily.
- The formation of small cracks between the fingers, affecting only the upper layers of the epidermis.
All these symptoms are not accompanied by itching or pain, so they do not cause discomfort to a person.
nail fungus
Toenail fungus is also a very common form of this disease. Such a fungus does not pose a particular threat to human health, but it can cause significant discomfort.
Nail Fungus Symptoms:
- The appearance of dryness and peeling of the skin of the feet.
- Itching.
- redness.
- Change in the shape of the nail.
- The color of the nails takes on a gray-yellow hue.
- cracking of the nail plate.
- brittleness of the nail.
- The formation of a crumbling mass under the nail.
- The formation of cavities under the nail plate.
- Bad smell.
When athlete's foot has become severe, the patient's temperature begins to rise. Athlete's foot, like any type of mycosis, can provoke the development of psoriasis or eczema.
What does skin fungus look like on the feet?
Although athlete's foot is a very common condition these days, not everyone knows exactly what it looks like. Many infected people don't even pay much attention when the first signs of a fungal infection appear. As already mentioned, there are different types of mushrooms.
Each type has its own symptoms:
- At the initial stage of infection, redness, slight swelling and cracks appear on the skin.
- In the middle stage of fungal development, peeling of the skin occurs. The foot is covered with white, pink or white spots.
- When the disease has already reached the highest degree of its development, the nail plates on the toes begin to collapse and change their usual color. The skin on the feet begins to peel off in large pieces. Deep and painful cracks develop.
A photo
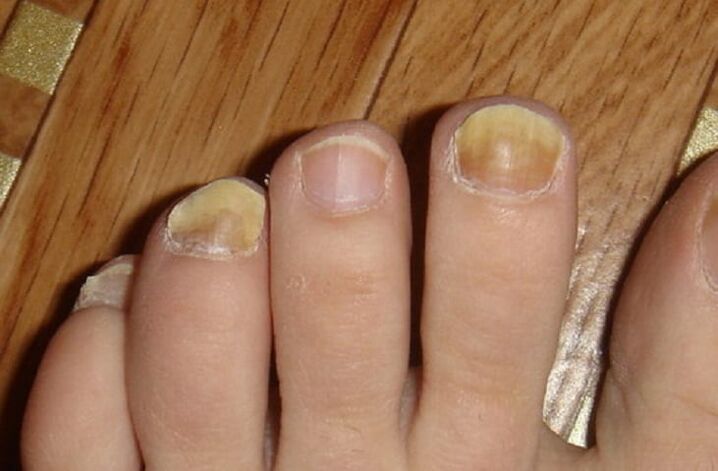
Symptoms of athlete's foot
To determine the fungus on the legs, attention must be paid to the basic symptoms:
- Reddening of the affected skin areas.
- exfoliation of the skin.
- Formation of bubbles with liquid content.
- Nails change color and shape.
- Fragility and delamination of the nail plate.
diagnosis
At the first manifestations of the symptoms of the fungus, you should consult a dermatologist. Sometimes a visual examination is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis.
Some symptoms may indicate the presence of another skin condition. Therefore, in such cases, a specialist should conduct scraping and microscopy. Only after such studies can we unequivocally speak about the presence and form of a fungal disease.
treatment
Treatment of a fungal disease must be started only after a full diagnosis by a specialist who will have to prescribe various drugs to treat this disease. Treatment of fungus on the legs can consist of several methods.
These methods include:
- systemic therapy.
- local therapy.
- home remedies.
It is worth considering each of them in more detail.
systemic therapy
Systemic therapy refers to the use of various antifungal drugs. Such drugs enter the bloodstream and kill the fungal infection. Such funds can penetrate the nail platinum, which can remain for several weeks, gradually killing the fungus.
Effective remedies against athlete's foot
Terbinafine and itraconazole are considered effective antifungal drugs. These systemic drugs can cure the patient in two weeks.
It is important to note that systemic therapy is not prescribed for the following people:
- Pregnant woman.
- breastfeeding mother.
- Individuals suffering from liver disease.
- Older people with comorbidities.
ointments and creams
It is recommended to combine systemic treatment of fungal diseases with local therapy. This treatment method includes various creams and ointments, which can also have an antifungal effect. However, it should be borne in mind that when using creams and ointments without systemic drugs, treatment may be ineffective.
Local drugs to fight fungal infections are divided into 20 forms. In addition to creams and ointments, various sprays, gels, foams and varnishes are also used to treat athlete's foot.
When treating the fungus locally, it should be remembered that after applying any agent to the skin, there is no need to wash the legs during the day.
home remedies
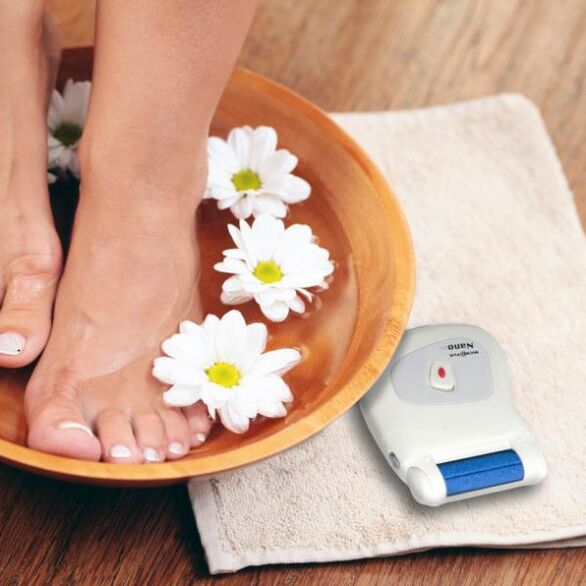

You can also cure the fungus of the skin of the feet with the help of folk remedies. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with them in more detail.
Folk remedies for treating nail fungus:
- A piece of kombucha is applied to the affected nails at night.
- Attach a cut Kalanchoe leaf to the nails overnight.
Folk remedies for treating fungus between the toes:
- Wash the skin between your fingers and grease with birch tar.
- Make a decoction of plantain, yarrow, wormwood and chamomile. Make foot baths from the prepared broth.
Folk remedies for treating athlete's foot:
- Lubricate the affected areas of the skin with onion juice at night.
- Make a night compress of propolis tincture 20%.
Folk remedies for treating athlete's foot:
- Do a sea salt foot bath twice a day.
- Take foot baths with a decoction of chamomile, oak bark and calendula three times a day.
prevention
The fungus of the skin of the legs most often causes sweating. Even in the cold season, the causative agent of a fungal disease is well preserved. But high temperature can kill the infection, so one of the methods of prevention is cooking. Another method of prevention is to disinfect shoes with formalin. With this action, the mushroom dies after 20 minutes.
Conclusion
Summing up, it is worth noting that fungal disease of the skin of the legs does not harm human health. The fungus only causes discomfort. However, this infection should not be ignored. If the disease becomes severe, it can lead to pain and the development of other infections.































